Section 2.2 Permutations
Subsection 2.2.1 Ordering Things
A number of applications of the rule of products are of a specific type, and because of their frequent appearance they are given their own designation, permutations. Consider the following examples.
How many different ways can we order the three different elements of the set \(A = \{a, b, c\}\text{?}\) Since we have three choices for position one, two choices for position two, and one choice for the third position, we have, by the rule of products, \(3 \cdot 2 \cdot 1 = 6\) different ways of ordering the three letters. We illustrate through a tree diagram.
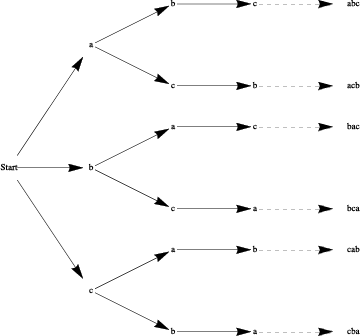
Each of the six orderings is called a permutation of the set \(A\text{.}\)
Example 2.2.3. Ordering a schedule.
A student is taking five courses in the fall semester. How many different ways can the five courses be listed? There are \(5 \cdot 4 \cdot 3 \cdot 2 \cdot 1 = 120\) different permutations of the set of courses.
In each of the above examples of the rule of products we observe that:
- We are asked to order or arrange elements from a single set.
- Each element is listed exactly once in each list (permutation). So if there are \(n\) choices for position one in a list, there are \(n - 1\) choices for position two, \(n - 2\) choices for position three, etc.
Example 2.2.4. Some orderings of a baseball team.
The alphabetical ordering of the players of a baseball team is one permutation of the set of players. Other orderings of the players’ names might be done by batting average, age, or height. The information that determines the ordering is called the key. We would expect that each key would give a different permutation of the names. If there are twenty-five players on the team, there are \(25 \cdot 24 \cdot 23 \cdot \cdots \cdot 3 \cdot 2 \cdot 1\) different permutations of the players.
This number of permutations is huge. In fact it is 15511210043330985984000000, but writing it like this isn’t all that instructive, while leaving it as a product as we originally had makes it easier to see where the number comes from. We just need to find a more compact way of writing these products.
We now develop notation that will be useful for permutation problems.
Definition 2.2.5. Factorial.
If \(n\) is a positive integer then \(n\) factorial is the product of the first \(n\) positive integers and is denoted \(n!\text{.}\) Additionally, we define zero factorial, \(0!\text{,}\) to be 1.
The first few factorials are
\begin{equation*}
\begin{array}{ccccccccc}
n & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 & 6 &
7 \\
n! & 1 & 1 & 2 & 6 & 24 & 120 &
720 & 5040 \\
\end{array}\text{.}
\end{equation*}
Note that \(4!\) is 4 times \(3!\text{,}\) or 24, and \(5!\) is 5 times \(4!\text{,}\) or 120. In addition, note that as \(n\) grows in size, \(n!\) grows extremely quickly. For example, \(11! = 39916800\text{.}\) If the answer to a problem happens to be \(25!\text{,}\) as in the previous example, you would never be expected to write that number out completely. However, a problem with an answer of \(\frac{25!}{23!}\) can be reduced to \(25 \cdot 24\text{,}\) or 600.
If \(\lvert A \rvert = n \text{,}\) there are \(n!\) ways of permuting all \(n\) elements of \(A\) . We next consider the more general situation where we would like to permute \(k\) elements out of a set of \(n\) objects, where \(k \leq n\text{.}\)
Example 2.2.6. Choosing Club Officers.
A club of twenty-five members will hold an election for president, secretary, and treasurer in that order. Assume a person can hold only one position. How many ways are there of choosing these three officers? By the rule of products there are \(25 \cdot 24 \cdot 23\) ways of making a selection.
Definition 2.2.7. Permutation.
An ordered arrangement of \(k\) elements selected from a set of \(n\) elements, \(0 \leq k \leq n\text{,}\) where no two elements of the arrangement are the same, is called a permutation of \(n\) objects taken \(k\) at a time. The total number of such permutations is denoted by \(P(n, k)\text{.}\)
Theorem 2.2.8. Permutation Counting Formula.
The number of possible permutations of \(k\) elements taken from a set of \(n\) elements is
\begin{equation*}
P(n,k)=n \cdot (n-1) \cdot (n-2) \cdot \cdots \cdot (n-k+1) = \prod_{j=0}^{k-1} (n-j) = \frac{n!}{(n-k)!} \text{.}
\end{equation*}
Proof.
Case I: If \(k = n\) we have \(P(n,n)=n!=\frac{n!}{(n-n)!}\text{.}\)
Case II: If \(0 \leq k < n\text{,}\)then we have \(k\) positions to fill using \(n\) elements and
- Position 1 can be filled by any one of \(n-0=n\) elements
- Position 2 can be filled by any one of \(n-1\) elements
- \(\displaystyle \cdots \)
- Position k can be filled by any one of \(n-(k-1)=n-k+1\) elements
Hence, by the rule of products,
\begin{equation*}
P(n,k) = n \cdot(n - 1) \cdot (n - 2) \cdot \cdots \cdot (n - k + 1) = \frac{n!}{(n-k)!}\text{.}
\end{equation*}
It is important to note that the derivation of the permutation formula given above was done solely through the rule of products. This serves to reiterate our introductory remarks in this section that permutation problems are really rule-of-products problems. We close this section with several examples.
Example 2.2.9. Another example of choosing officers.
A club has eight members eligible to serve as president, vice-president, and treasurer. How many ways are there of choosing these officers?
Solution 1: Using the rule of products. There are eight possible choices for the presidency, seven for the vice-presidency, and six for the office of treasurer. By the rule of products there are \(8 \cdot 7\cdot 6 = 336\) ways of choosing these officers.
Solution 2: Using the permutation formula. We want the total number of permutations of eight objects taken three at a time:
\begin{equation*}
P(8,3)=\frac{8!}{(8-3)!}=8 \cdot 7 \cdot 6 = 336
\end{equation*}
Example 2.2.10. Course ordering, revisited.
To count the number of ways to order five courses, we can use the permutation formula. We want the number of permutations of five courses taken five at a time:
\begin{equation*}
P(5,5)= \frac{5!}{(5-5)!}= 5!= 120\text{.}
\end{equation*}
Example 2.2.11. Ordering of digits under different conditions.
Consider only the digits 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5.
- How many three-digit numbers can be formed if no repetition of digits can occur?
- How many three-digit numbers can be formed if repetition of digits is allowed?
- How many three-digit numbers can be formed if only non-consecutive repetition of digits are allowed?
Solutions to (a): Solution 1: Using the rule of products. We have any one of five choices for digit one, any one of four choices for digit two, and three choices for digit three. Hence, \(5 \cdot 4 \cdot 3 = 60\) different three-digit numbers can be formed.
Solution 2; Using the permutation formula. We want the total number of permutations of five digits taken three at a time:
\begin{equation*}
P(5,3)=\frac{5!}{(5-3)!}=5 \cdot 4 \cdot 3 = 60\text{.}
\end{equation*}
Solution to (b): The definition of permutation indicates “...no two elements in each list are the same.” Hence the permutation formula cannot be used. However, the rule of products still applies. We have any one of five choices for the first digit, five choices for the second, and five for the third. So there are \(5 \cdot 5\cdot 5 = 125\) possible different three-digit numbers if repetition is allowed.
Solution to (c): Again, the rule of products applies here. We have any one of five choices for the first digit, but then for the next two digits we have four choices since we are not allowed to repeat the previous digit So there are \(5 \cdot 4\cdot 4 = 80\) possible different three-digit numbers if only non-consecutive repetitions are allowed.
Exercises 2.2.2 Exercises
1.
If a raffle has three different prizes and there are 1,000 raffle tickets sold, how many different ways can the prizes be distributed?
Answer.
\(P(1000,3)\)
2.
- How many three-digit numbers can be formed from the digits 1, 2, 3 if no repetition of digits is allowed? List the three-digit numbers.
- How many two-digit numbers can be formed if no repetition of digits is allowed? List them.
- How many two-digit numbers can be obtained if repetition is allowed?
3.
How many eight-letter words can be formed from the 26 letters in the alphabet? Even without concerning ourselves about whether the words make sense, there are two interpretations of this problem. Answer both.
Answer.
With repetition: \(26^8\approx 2.0883\times 10^{11}\)
Without repetition: \(P(26,8) \approx 6.2991\ 10^{10}\)
4.
Let \(A\) be a set with \(\lvert A \rvert = n \text{.}\) Determine
- \(\displaystyle \lvert A^3 \rvert \)
- \(\displaystyle \lvert \{ (a, b, c) \mid a, b, c \in A \textrm{ and each coordinate is different}\} \rvert \)
5.
The state finals of a high school track meet involves fifteen schools. How many ways can these schools be listed in the program?
Answer.
\(15!\)
6.
Consider the three-digit numbers that can be formed from the digits 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 with no repetition of digits allowed.
a. How many of these are even numbers?
b. How many are greater than 250?
7.
All 15 players on the Tall U. basketball team are capable of playing any position.
- How many ways can the coach at Tall U. fill the five starting positions in a game?
- What is the answer if the center must be one of two players?
Answer.
- \(\displaystyle P(15,5)=360360\)
- \(\displaystyle 2\cdot 14\cdot 13\cdot 12\cdot 11=48048\)
8.
- How many ways can a gardener plant five different species of shrubs in a circle?
- What is the answer if two of the shrubs are the same?
- What is the answer if all the shrubs are identical?
9.
The president of the Math and Computer Club would like to arrange a meeting with six attendees, the president included. There will be three computer science majors and three math majors at the meeting. How many ways can the six people be seated at a circular table if the president does not want people with the same majors to sit next to one other?
Answer.
\(2\cdot P(3,3)=12\)
10.
Six people apply for three identical jobs and all are qualified for the positions. Two will work in New York and the other one will work in San Diego. How many ways can the positions be filled?
11.
Let \(A = \{1, 2, 3, 4\} \text{.}\) Determine the cardinality of
- \(\displaystyle \{ (a_1,a_2) \mid a_1 \neq a_2 \}\)
- What is the answer to the previous part if \(\lvert A \rvert = n\)
- If \(\lvert A \rvert =n\text{,}\) determine the number of \(m\)-tuples in \(A\text{,}\) \(m \leq n\text{,}\) where each coordinate is different from the other coordinates.
Answer.
- \(\displaystyle P(4,2)=12\)
- \(\displaystyle P(n;2)=n(n-1)\)
-
Case 1: \(m>n\text{.}\) Since the coordinates must be different, this case is impossible.Case 2: \(m\leqslant n. P(n;m)\text{.}\)

